1. Importance of IAQ
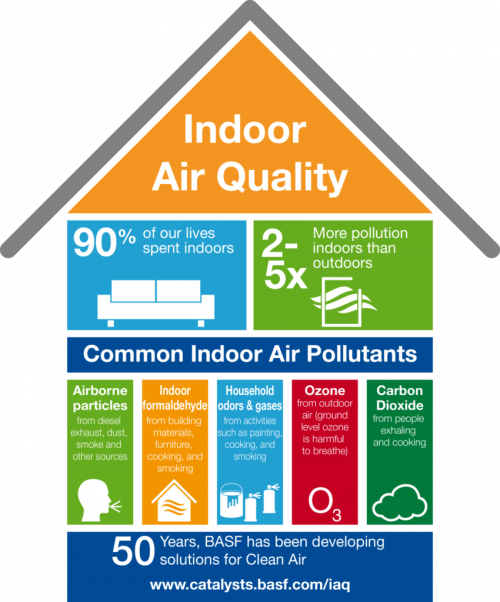
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) refers to the air characteristics inside a building that affect the health, comfort, and productivity of occupants. Poor IAQ can lead to sick building syndrome (SBS), increased absenteeism, and reduced efficiency.
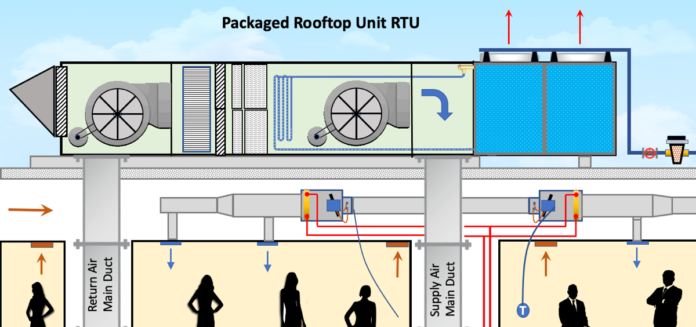
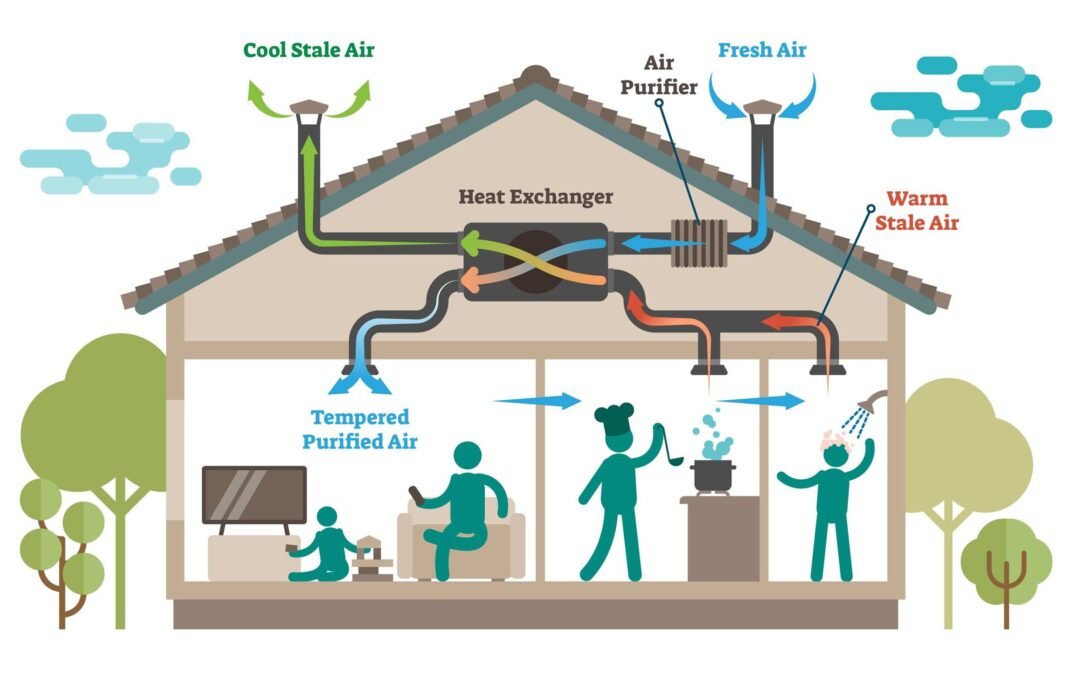
FAHUs play a crucial role in maintaining IAQ by supplying filtered, conditioned, and controlled outdoor air.
2. Key IAQ Parameters
🔹 a. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Levels
- Source: Occupant respiration, combustion equipment, overcrowding.
- Acceptable Limit:
- ASHRAE Standard 62.1 recommends indoor CO₂ levels should not exceed 700 ppm above outdoor levels (usually keeping indoor levels < 1000 ppm).
- Impact:
- High CO₂ → drowsiness, headaches, reduced concentration, poor decision-making.
- FAHU Role:
- Provides sufficient fresh air to dilute CO₂.
- Integrated with CO₂ sensors + demand-controlled ventilation (DCV) to adjust airflow.
🔹 b. Contaminants & Particulate Matter
- Types of Contaminants:
- Dust and pollen → cause allergies, asthma.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): from paints, cleaning products, furniture.
- Microbial contaminants: bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold spores.
- Smoke and odors.
- Acceptable Levels:
- PM2.5 (particles <2.5 µm) should be < 12 µg/m³ (annual mean) per WHO.
- VOC levels vary, but benzene, formaldehyde, and toluene should be kept as low as possible.
- FAHU Role:
- Multi-stage filtration (Pre-filter, Fine filter, HEPA filter in healthcare).
- Optional UV-C lamps or ionization for microbial control.
- Ensures clean outdoor air supply even in polluted urban environments.
🔹 c. Humidity Levels
- Optimal Range:
- 40% – 60% Relative Humidity (RH) (per ASHRAE & WHO).
- Impact of Low Humidity (<30% RH):
- Dry eyes, skin irritation, respiratory discomfort.
- Static electricity buildup in electronics.
- Impact of High Humidity (>70% RH):
- Mold growth, condensation, material damage.
- Increased survival of microbes.
- FAHU Role:
- Cooling coils → dehumidify hot, humid outdoor air.
- Humidifiers → add moisture in dry climates.
- Controls humidity before air enters occupied spaces.
3. Other IAQ Parameters (Secondary but Important)
- Temperature: 22–25°C comfort range.
- Airborne microbes: Critical in hospitals, labs.
- Air Changes per Hour (ACH): Higher ACH = cleaner air (hospitals, labs, cleanrooms).
- Odors: Controlled by ventilation and activated carbon filters.
4. Example: Office Environment
- Outdoor air CO₂ = 400 ppm → indoor target < 1000 ppm.
- FAHU ensures 15–20 CFM/person of fresh air as per ASHRAE 62.1.
- Filters reduce dust and pollen levels.
- Cooling coil dehumidifies air from 80% RH (humid summer) to ~50% RH indoor comfort.
5. Example: Hospital ICU
- CO₂ levels kept < 800 ppm.
- FAHU with HEPA filters and UV-C ensures sterile supply.
- Humidity maintained at 50–55% RH to prevent microbial growth.
- Positive pressure maintained relative to corridors.