1. Why Pressure Control Matters
- Buildings are not just about temperature; they also need controlled air movement between spaces.
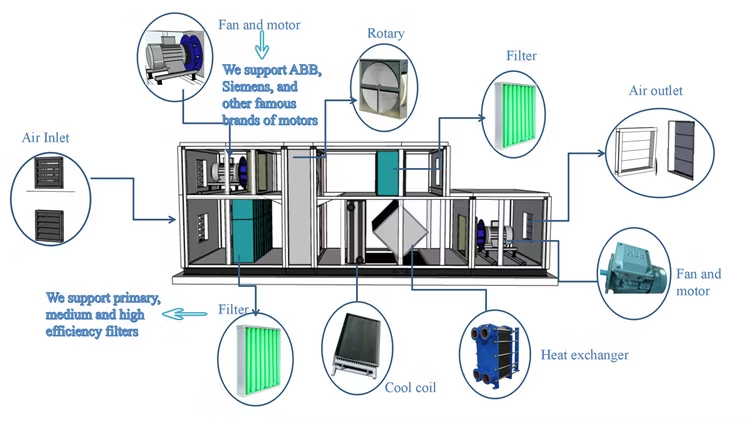
- FAHUs supply 100% outdoor air, which is the primary lever for establishing pressure differentials.
- By adjusting supply air vs. exhaust air volumes, FAHUs help maintain:
- Positive pressure in clean/safe areas.
- Negative pressure in contaminated/hazardous areas.
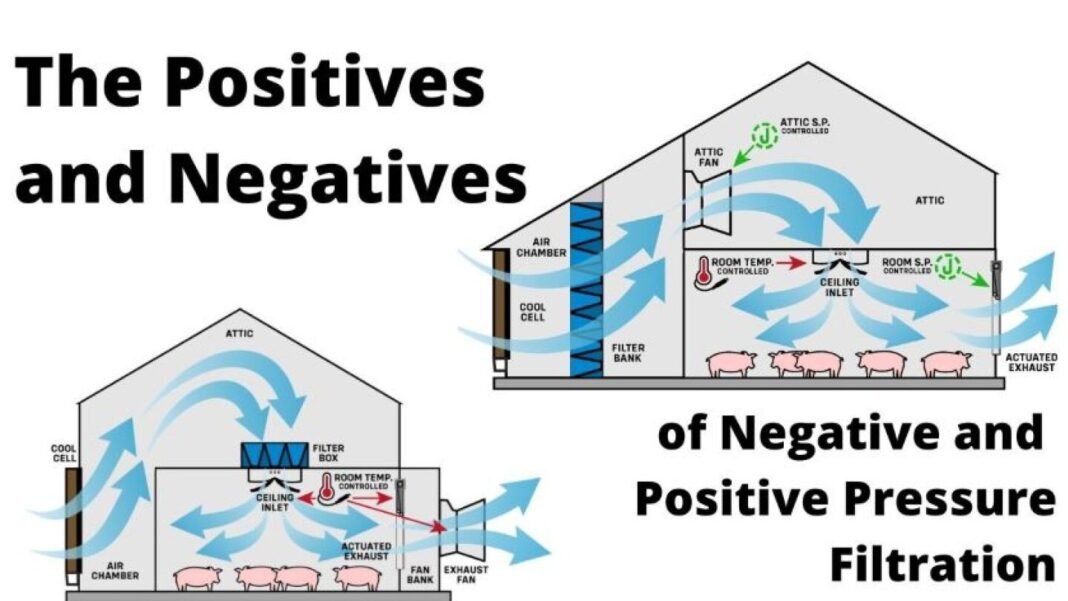
2. FAHU in Positive Pressure Control
Definition:
Positive pressure exists when supply airflow > exhaust airflow, causing air to flow outward when doors or leaks occur.
FAHU Role:
- Delivers a continuous stream of conditioned outdoor air into the zone.
- Slightly oversupplies air compared to return/exhaust systems.
- Maintains healthy, filtered air inside, preventing infiltration of dust, smoke, or pollutants.
Applications:
- Healthcare:
- Operating Rooms (ORs): FAHU supplies sterile filtered air to maintain +15 Pa relative to adjacent spaces.
- ICUs and clean wards.
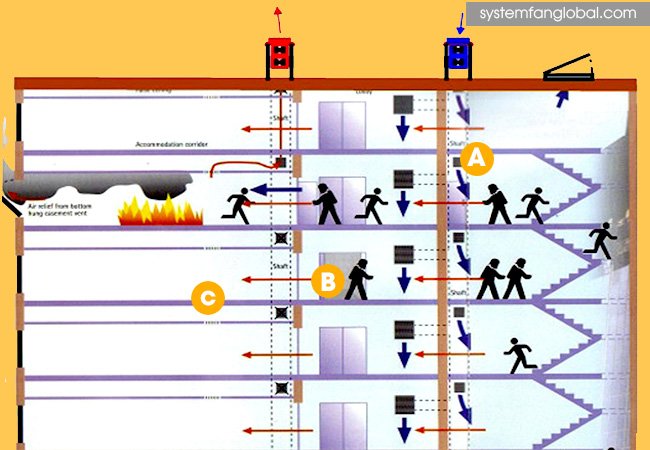
- Commercial High-Rise:
- Lift lobbies and stairwells are pressurized via FAHU during fire events to prevent smoke entry.
- Data Centers & Cleanrooms:
- Keeps contaminants out by pressurizing equipment spaces.
3. FAHU in Negative Pressure Control
Definition:
Negative pressure exists when exhaust airflow > supply airflow, causing air to flow inward when doors or leaks occur.
FAHU Role:
- Supplies controlled fresh air, but the exhaust system is designed to exceed supply.
- FAHU ensures fresh air enters, but contaminated air is pulled out and safely discharged.
- Helps contain hazards by preventing air from leaking out.
Applications:
- Healthcare:
- Isolation Rooms (TB, COVID wards): FAHU supplies filtered air, while exhaust fans maintain –15 Pa relative to corridors.
- Industrial & Labs:
- Chemical laboratories, fume hood areas.
- Pharmaceutical production with hazardous by-products.
- Kitchens & Toilets:
- FAHU provides make-up air while exhaust maintains negative pressure.
4. How FAHUs Achieve Pressure Control
- Airflow Balancing: FAHU supply is coordinated with exhaust/return air fans.
- Differential Pressure Sensors: Continuously monitor room pressure; signals sent to FAHU dampers/fans.
- BMS Integration: Building Management System adjusts FAHU fan speed (VFDs) to maintain setpoint pressure.
- Airlocks & Cascade Design: FAHUs ensure correct airflow direction by maintaining cascaded pressures (e.g., OR → corridor → utility zone).
5. Practical Example
Hospital Wing with FAHU:
- Operating Theater (OT):
- FAHU supplies 100% HEPA-filtered air at +15 Pa positive pressure.
- Prevents bacteria from corridors entering OT.
- Isolation Room:
- FAHU supplies air, but exhaust > supply → –15 Pa negative pressure.
- Prevents infectious air from leaking into adjacent areas.
6. Typical Pressure Differentials Maintained by FAHU
| Application | Pressure Requirement |
|---|---|
| Hospital Operating Room | +15 Pa (Positive) |
| ICU / Clean Room | +5 to +10 Pa (Positive) |
| Hospital Isolation Room | –15 Pa (Negative) |
| Toilets / Bathrooms | –10 Pa (Negative) |
| Stairwells (Fire Mode) | +25 to +50 Pa (Positive) |