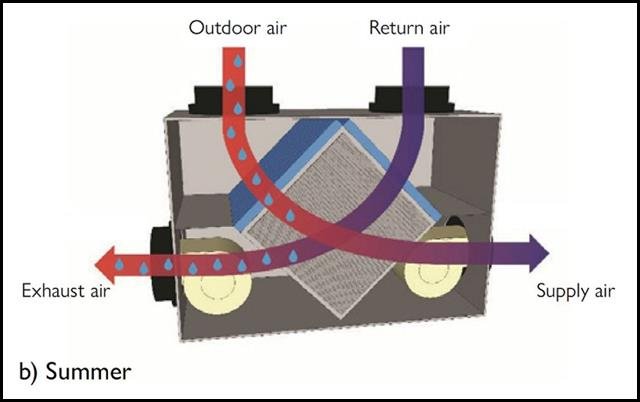
1. Role of Coils in FAHU
- FAHUs handle 100% outdoor air, which must be conditioned before supply.
- Cooling Coils → reduce temperature and remove humidity.
- Heating Coils → increase temperature or reheat dehumidified air.
- Together, they ensure thermal comfort, humidity control, and process requirements.
2. Cooling Coils
Function
- Lower the temperature of hot outdoor air.
- Condense and remove excess moisture (dehumidification).
- Maintain comfort and IAQ by supplying air within set temperature & humidity.
Types
- Chilled Water (CHW) Coil:
- Uses chilled water from central chiller plant.
- Common in large commercial/industrial systems.
- Direct Expansion (DX) Coil:
- Uses refrigerant (R-410A, R-32, etc.) from condensing unit.
- Used in smaller systems or where no chiller plant exists.
Design Considerations
- Capacity: Based on required cooling load (sensible + latent).
- Face Velocity: Typically 2–2.5 m/s (400–500 FPM).
- Rows of Tubes: 4–8 rows depending on load.
- Fin Material: Aluminum (common), Copper (better conductivity, higher cost).
- Condensate Drain Pan: Must be sloped and corrosion-resistant to avoid water carryover.
3. Heating Coils
Function
- Heat cold outdoor air in winter climates.
- Provide reheat after dehumidification (for humidity control).
- Maintain minimum supply air temperature to occupied zones.
Types
- Hot Water Coil:
- Uses hot water from boiler or district heating.
- Steam Coil:
- Uses steam (industrial applications, cold climates).
- Electric Heater Coil:
- Used where hot water/steam is not available (backup heating).
Design Considerations
- Supply Air Temperature: Usually 20–22°C (68–72°F) in comfort applications.
- Materials: Copper tubes, aluminum fins, galvanized/stainless casing.
- Freeze Protection: Required for coils in cold climates (glycol mixture or preheat coil).
4. Psychrometric Role
- Cooling Coil Process: Air follows a cooling + dehumidification line on the psychrometric chart (downward & left).
- Heating Coil Process: Air follows a sensible heating line (upward, constant humidity ratio).
- Reheat Process: After deep dehumidification, heating coil raises dry-bulb temperature without adding moisture.
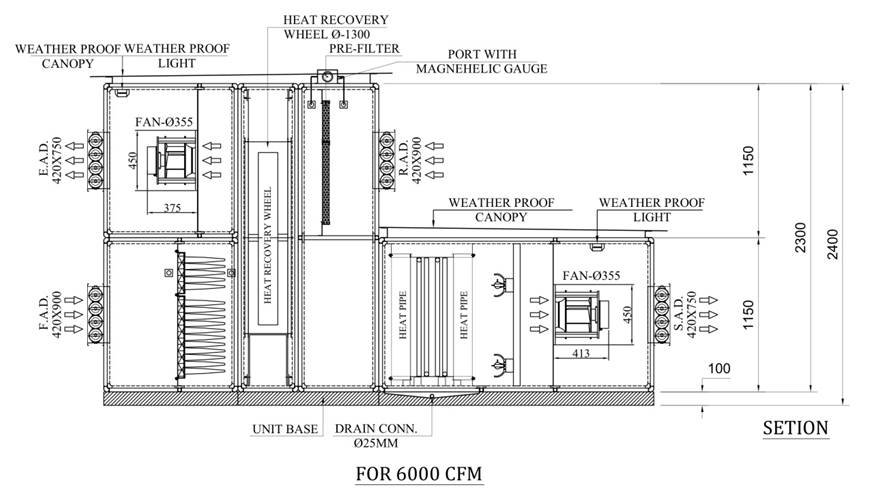
5. Coil Placement in FAHU
- Filter → Cooling Coil → Heating Coil → Fan
- Cooling coils are placed before fans to handle conditioned air.
- Heating coils may be:
- Preheat coils (before filters) → prevent freezing in cold climates.
- Reheat coils (after cooling coil) → humidity & comfort control.
6. Pressure Drop & Maintenance
- Cooling coils: Add 50–100 Pa pressure drop.
- Heating coils: Add 30–70 Pa pressure drop.
- Maintenance:
- Regular coil cleaning to prevent fouling (dust, biofilm).
- Ensure drain pans are clean to avoid microbial growth.
- Inspect fins & straighten bent sections.
7. Applications
- Office Buildings: Cooling coil (CHW/DX) + optional reheat coil.
- Hospitals: Cooling coil for temperature + humidity control, reheat coil for sterile supply.
- Cold Regions: Preheat coil to prevent frosting of filters and coils.
- Pharma/Labs: Combination of cooling + heating coils for precise air treatment.
8. Example Case
- Outdoor Air: 38°C DB / 26°C WB (hot-humid climate).
- Desired Supply: 22°C DB / 50% RH.
- Cooling Coil: Drops air to 14°C (dehumidification to remove moisture).
- Heating Coil (Reheat): Raises air back to 22°C at ~50% RH → comfort condition.