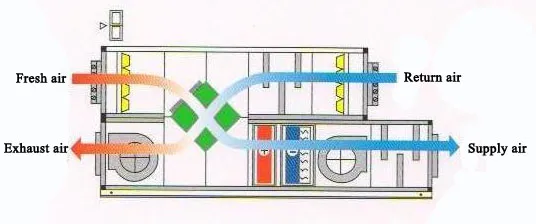
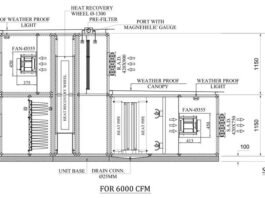
1. Role of Fans in FAHU
- Move conditioned outdoor air through filters, coils, and ducts into the building.
- Overcome system static pressure (filters, coils, silencers, ductwork).
- Ensure design airflow to maintain IAQ, comfort, and pressurization.
2. Types of Fans Used in FAHU
🔹 a. Centrifugal Fans
- How They Work: Air enters axially into the fan wheel and exits radially.
- Types:
- Forward-curved: Low noise, lower efficiency.
- Backward-curved: Higher efficiency, widely used in AHUs/FAHUs.
- Airfoil blades: Highest efficiency, lower noise.
- Advantages:
- High static pressure capability (500–2000 Pa).
- Robust and reliable.
- Applications: Large FAHUs, hospitals, commercial towers.
🔹 b. Plug Fans (Plenum Fans)
- How They Work: Fan wheel sits directly in the plenum (chamber) without scroll housing.
- Advantages:
- Compact, easy to integrate in modular FAHUs.
- Direct-drive (no belts) → less maintenance.
- Even airflow distribution across coil/filter face.
- Efficiency: Medium-high.
- Applications: Modern FAHUs in malls, airports, data centers.
🔹 c. EC Fans (Electronically Commutated Fans)
- How They Work: Brushless DC motors with built-in electronic control.
- Advantages:
- Very high efficiency (up to 90%).
- Variable speed control (no need for separate VFD).
- Quiet operation.
- Smaller footprint.
- Applications: Energy-efficient buildings, green projects, retrofits.
- Standards: Often used where LEED/WELL/Estidama compliance is required.
3. Fan Selection Criteria
- Airflow Capacity (CFM or L/s).
- Static Pressure Requirement (Pa or in. w.g.).
- Efficiency (fan curves).
- Noise Level (NC values for comfort spaces).
- Space/installation constraints.
- Maintenance requirements.
4. Fan Control & Integration
- VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives): Used with centrifugal/plug fans for speed control and energy saving.
- EC Fans: Have built-in speed control, BMS-ready.
- Pressure Sensors: Linked to fans to maintain constant airflow under varying filter pressure drops.
- BMS Monitoring: Energy use, alarms, and performance tracking.
5. Pressure Drop & Maintenance
- Contribution: Fans must overcome ~300–600 Pa FAHU resistance + duct pressure drop.
- Maintenance Tasks:
- Inspect bearings, belts (for belt-driven fans).
- Lubricate bearings as per manufacturer’s instructions.
- Clean fan blades and housings to avoid imbalance.
- Check vibration and noise.
- For EC fans: Check electronic boards, sensors, and clean cooling vents.
6. Comparison Table
| Fan Type | Efficiency | Pressure Capability | Noise | Maintenance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal | Medium–High | High (500–2000 Pa) | Moderate | Moderate (belts, bearings) | Large FAHUs, hospitals |
| Plug Fan | Medium–High | Medium (300–1000 Pa) | Lower | Low (direct-drive) | Modular FAHUs, data centers |
| EC Fan | Very High | Medium (300–1000 Pa) | Very Low | Very Low (no belts) | Energy-efficient, green buildings |
7. Example Applications
- Hospital FAHU: Centrifugal backward-curved fans to handle high filter pressure (HEPA).
- Shopping Mall FAHU: Plug fans for large airflow and even coil face distribution.
- Office Tower FAHU (LEED Certified): EC fans for maximum energy efficiency and BMS integration.