1. Importance of Filters
- Protect occupants by removing dust, pollen, smoke, bacteria, and harmful particles.
- Protect downstream HVAC components (coils, ducts, diffusers) from clogging and fouling.
- Improve Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) and comply with ASHRAE 62.1, EN 779, ISO 16890 standards.
- Different spaces (office vs. hospital) require different filtration levels.
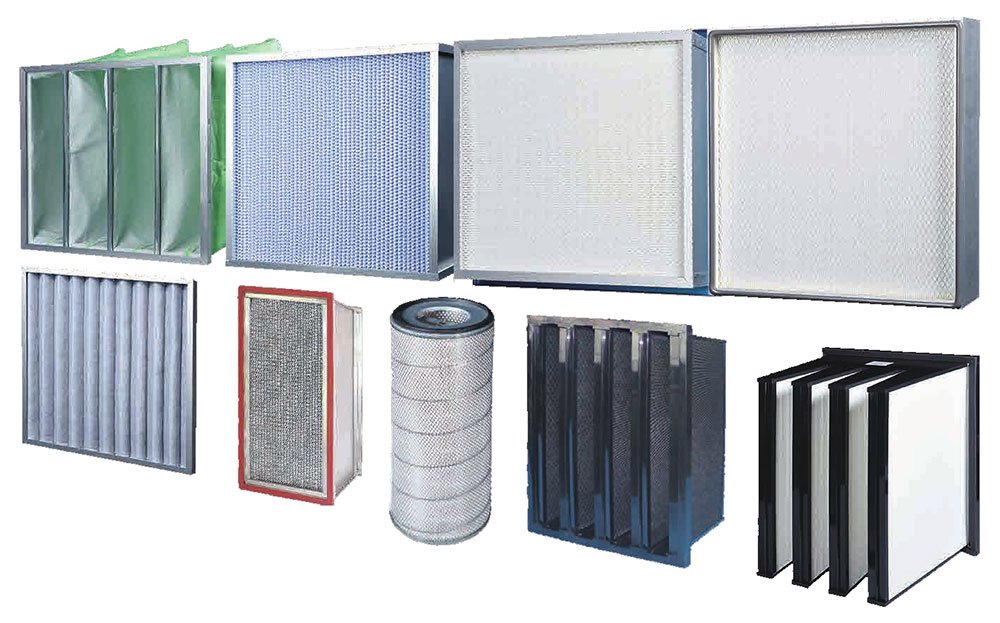
2. Types of Filters in FAHU
🔹 a. Pre-Filters
- Efficiency: Low efficiency (MERV 4–8 / G2–G4 in EN standard).
- Particle Size Removed: Large particles >10 µm (dust, lint, pollen, hair).
- Material: Washable synthetic fibers, aluminum mesh, or nonwoven fabric.
- Purpose:
- First line of defense against coarse dust.
- Extends life of fine and HEPA filters.
- Applications: Used in all FAHUs as the primary stage.
🔹 b. Fine Filters (Secondary Filters)
- Efficiency: Medium to high (MERV 9–13 / F5–F9 in EN standard).
- Particle Size Removed: 1–10 µm (smaller dust, bacteria carriers, smoke).
- Material: Pleated synthetic fiber or glass fiber media.
- Purpose:
- Improves IAQ by removing smaller particles.
- Protects sensitive areas and equipment.
- Applications:
- Offices, malls, airports (F7–F8).
- Healthcare general areas (F9).
🔹 c. HEPA Filters (High-Efficiency Particulate Air)
- Efficiency: ≥99.97% at 0.3 µm particle size (H13, H14 in EN 1822).
- Particle Size Removed: Very fine particles including bacteria, viruses, smoke, allergens.
- Material: Ultra-fine glass fibers arranged in pleats.
- Purpose:
- Critical for sterile environments.
- Ensures protection from airborne infections.
- Applications:
- Hospital operating rooms, isolation rooms, ICUs.
- Pharmaceutical production & cleanrooms.
- Labs requiring contamination-free environments.
3. Filter Arrangement in FAHU
Filters are arranged in stages to maximize efficiency and lifespan:
- Pre-Filter (Coarse) → Captures large particles.
- Fine Filter (Secondary) → Captures medium to small particles.
- HEPA Filter (Final) → Installed only in critical applications.
🔹 Example:
- Office FAHU: Pre-filter + Fine filter (F7).
- Hospital FAHU: Pre-filter + Fine filter (F9) + HEPA filter (H13/H14).
4. Pressure Drop & Maintenance
- Each filter creates resistance (pressure drop) to airflow.
- Pressure drop increases as the filter gets dirty.
- Differential Pressure Gauges or sensors are used to indicate replacement time.
- Maintenance:
- Pre-filters → washable, replaced every 3–6 months.
- Fine filters → replaced every 6–12 months.
- HEPA filters → replaced every 1–2 years (depending on usage).
5. Comparison Table
| Filter Type | Efficiency (MERV/EN/ISO) | Particles Removed | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Filter | MERV 4–8 / G2–G4 | >10 µm (dust, lint, pollen) | All FAHUs (basic protection) |
| Fine Filter | MERV 9–13 / F5–F9 | 1–10 µm (smoke, bacteria carriers) | Offices, airports, malls |
| HEPA Filter | H13–H14 / ≥99.97% at 0.3 µm | <1 µm (bacteria, viruses) | Hospitals, cleanrooms, pharma |
6. Practical Example
- Hospital Operating Room FAHU:
- Pre-filter (MERV 8) → removes dust/pollen.
- Fine filter (F9) → removes bacteria carriers.
- HEPA filter (H14) → delivers sterile air to OT.
- Office Tower FAHU:
- Pre-filter (MERV 6).
- Fine filter (F7).
- No HEPA (not required, saves energy).