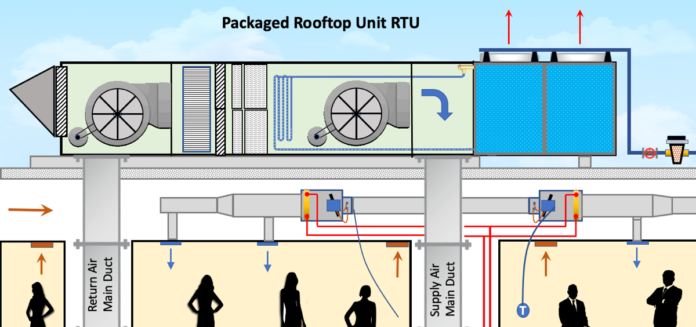
1. Fresh Air (Outdoor Air)
- Definition: Air brought into the building from outdoors.
- Purpose:
- Replaces stale indoor air.
- Maintains acceptable Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) by diluting CO₂, VOCs, odors, and contaminants.
- Provides oxygen for occupants.
- Treatment: Must be filtered, cooled/heated, and dehumidified/humidified before supply.
- Supplied By: FAHU (100% fresh air) or AHU (mix of fresh + return air).
- Example: In an office, outdoor air is brought in through FAHU, cooled, filtered, and then mixed with return air in AHU before distribution.
2. Return Air
- Definition: Indoor air that is drawn back from the occupied space to the AHU.
- Purpose:
- Saves energy by recirculating conditioned air instead of conditioning 100% fresh air.
- A portion of return air is mixed with fresh air in AHU to maintain comfort and reduce cooling/heating load.
- Handling: Often passes through filters again before re-entering the AHU mixing box.
- Example: In a mall, air from shops and corridors is returned to the AHU, mixed with 20–30% fresh air, and then supplied again.
3. Exhaust Air
- Definition: Indoor air that is removed and discharged outdoors through fans or ducts.
- Purpose:
- Removes contaminants, odors, humidity, and harmful gases from specific areas.
- Maintains correct air balance (especially in toilets, kitchens, labs).
- Special Cases:
- Toilet and kitchen exhausts are always 100% discharged (never recirculated).
- In healthcare, isolation rooms use dedicated exhaust systems with HEPA filters.
- Example: In a hospital isolation ward, contaminated air is exhausted to the outside after HEPA filtration.
4. Relationship Between Fresh, Return, and Exhaust Air
- Air Balance Principle:
- Supply Air = Fresh Air + Return Air – Exhaust Air
- The ratio is designed to maintain IAQ, comfort, and building pressurization.
- Typical Ratios (varies by code & application):
- Offices: ~20% fresh air + 80% return air
- Hospitals: ~100% fresh air (critical spaces)
- Kitchens/Toilets: 100% exhaust
5. Comparison Table
| Air Type | Source | Purpose | Recirculated? | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Air | Outdoor atmosphere | Dilute CO₂, maintain IAQ, supply oxygen | No (always conditioned) | FAHU, AHU |
| Return Air | Indoor occupied spaces | Energy saving, reuse conditioned air | Yes (partly recirculated) | AHU mixing |
| Exhaust Air | Indoor occupied/specific zones | Remove contaminants, odors, humidity | No (always discharged) | Toilets, labs, kitchens |
6. Case Example: Office Building
- Fresh Air: 20% outdoor air brought by FAHU → filtered, cooled, supplied to AHU.
- Return Air: 80% air collected from occupied spaces → mixed with fresh air in AHU.
- Exhaust Air: Small percentage (10–20%) discharged outside → ensures proper air balance and prevents buildup of pollutants.